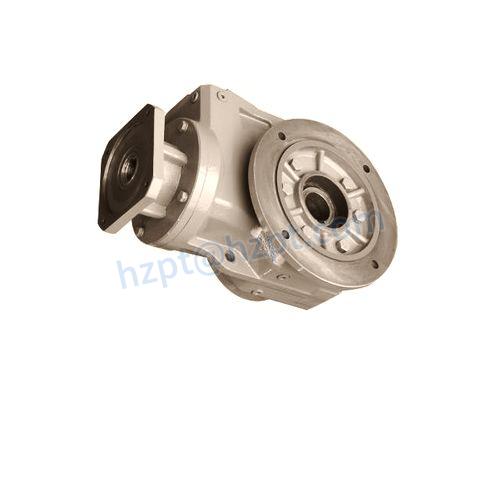
Product Description
Flange Input Right Angle Big Output Torque Planetary Transmission Gearbox With Motor
Description:
N series of planetary reducers from SGR are widely used for industrial and heavy duty severe applications . planetary reducer feature with compact size, low noise , excellent reliability ,long life . In-line or right-angle planetary gearboxes are available in male and female shaft configurations. The CHINAMFG male shaft solution (splined or cylindrical) is able to withstand strong radial or axial loads on the output shaft. As a leading planetary gearbox manufactory in China , SGR planetary reducer is produced by modular design, combined according to customer requirement, housing material from CHINAMFG with nodular cast iron which can increases gearbox’s rigidity and antiknock, heavy-duty bearing is installed at low-speed shaft, it can bear big radial load due to proportionate distribution of torque ,every CHINAMFG gears are case hardened to get high reliability and long life . SGR planetary reducer have 16 models for different torque range ,each CHINAMFG model have 1-5 stages to achieve different ratios , SGR planetary reducer have wide rang selection of high speed design: cylindrical with key, hydraulic motor, electric motor .Installation in CHINAMFG is multiposition ,various fasten type .
N series planetary gearbox torque sheet with models
| Gear unit size | 200 | 201 | 240 | 241 | 280 | 281 | 353/354 | 355 | 400 | 401 |
| Normal output torque T2N[Nm] |
1500 | 2000 | 3500 | 4000 | 4300 | 7300 | 13000 | 16000 | 20000 | 23000 |
| Gear unit size | 428 | 429 | 445 | 446 | 510 | 542 | 543 | 695 | 810 | 885 |
| Normal output torque T2N[Nm] |
26000 | 30000 | 32000 | 43000 | 63000 | 75000 | 100000 | 150000 | 300000 | 420000 |
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Industry |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Hardness: | Hardened |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |
| Step: | Four-Step |
| Samples: |
US$ 500/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Choosing Lubrication for Angle Gearboxes
When selecting lubrication for angle gearboxes, several critical considerations should be taken into account:
- Operating Conditions: The operating environment, temperature range, and exposure to moisture or contaminants play a significant role in determining the type of lubricant needed.
- Load and Torque: The load-carrying capacity and torque requirements of the gearbox impact the choice of lubricant viscosity and additives.
- Speed: The speed of the gearbox influences the lubricant’s ability to form and maintain a protective film between gear surfaces.
- Materials: Consider the materials of the gears, bearings, and other components to ensure compatibility with the lubricant.
- Lubricant Type: Choose between oil and grease lubrication, considering factors like lubrication intervals, leakage, and sealing effectiveness.
- Viscosity: The lubricant’s viscosity should match the gearbox’s operational requirements, providing sufficient film thickness without causing excessive drag.
- Extreme Conditions: In extreme temperatures or harsh conditions, specialized lubricants with additives for high-temperature, low-temperature, or extreme-pressure performance may be necessary.
- Sealing: The gearbox’s sealing effectiveness impacts lubricant retention and protection against contaminants.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the chosen lubricant is compatible with any existing lubricants or residues to prevent chemical reactions.
- Maintenance: Consider ease of lubricant replenishment and maintenance intervals when selecting a lubrication solution.
Choosing the appropriate lubrication for angle gearboxes is essential to ensure smooth operation, minimize wear and friction, extend the gearbox’s lifespan, and maintain overall efficiency and reliability.

Impact of Gear Ratios on Performance of Angle Gearboxes
Gear ratios play a significant role in determining the performance of angle gearboxes. The gear ratio is a measure of how many revolutions the input shaft makes compared to the output shaft. Here’s how gear ratios impact the performance:
Torque and Speed Relationship: The gear ratio directly affects the relationship between torque and speed. In an angle gearbox, a higher gear ratio (such as 1:5) means that the output shaft will rotate fewer times than the input shaft but with greater force. Conversely, a lower gear ratio (such as 5:1) results in the output shaft spinning more times but with less force. This relationship is crucial for adapting the gearbox to specific application requirements.
Power Transmission: The right choice of gear ratio ensures efficient power transmission. If a high torque is required, a lower gear ratio is chosen to provide mechanical advantage. On the other hand, a higher gear ratio is selected for applications where higher rotational speed is essential. The gear ratio determines how effectively the gearbox can convert input power into the desired output power.
Application Adaptation: Gear ratios allow angle gearboxes to adapt to various applications. Different tasks require different combinations of torque and speed. By selecting the appropriate gear ratio, the gearbox can tailor its output to suit the specific demands of the task, optimizing efficiency and performance.
Overall, gear ratios in angle gearboxes provide a way to fine-tune the output characteristics, allowing them to fulfill a wide range of mechanical requirements across different industries and applications.
Handling Variations in Input and Output Angles with Angle Gearboxes
Angle gearboxes are specifically designed to handle variations in input and output angles, allowing for efficient redirection of rotational motion. They achieve this through the use of bevel gears and hypoid gears. Here’s how they handle such variations:
- Bevel Gears: Angle gearboxes equipped with bevel gears can handle changes in input and output angles by using intersecting axes. These gears have conical shapes and teeth that are cut along the cone surface. When the input shaft’s bevel gear meshes with the output shaft’s bevel gear, the intersecting angles allow for smooth power transmission even when the axes are not aligned.
- Hypoid Gears: Hypoid gear arrangements in angle gearboxes can handle larger variations in input and output angles compared to bevel gears. Hypoid gears have helical teeth and axes that are offset from each other. This offset allows for greater flexibility in handling non-parallel input and output shafts.
By employing these gear types, angle gearboxes can effectively manage variations in input and output angles, ensuring that rotational motion is smoothly redirected without compromising efficiency or causing excessive wear on the gears.


editor by CX 2023-10-30
